The Z-Papers on the SCIENCE WARS Part 2
Herb Zinser explains the social science wars of atoms, math equations, biochemistry molecules, television photons, English language nouns and symbol life in the battle to control civilization.
Concept Paper CP-160 by Herb Zinser on math warrior Joan of ARC(sin) who had committed sin


Joan of Arc
Joan of Arc (French: Jeanne d’Arc,[4] IPA: [ʒan daʁk]; ca. 1412[5] – 30 May 1431), nicknamed “The Maid of Orléans” (French: La Pucelle d’Orléans), is considered a heroine of France and a Roman Catholic saint. She was born to a peasant family at Domrémy in north-east France. Joan said she received visions of the Archangel Michael, Saint Margaret and Saint Catherine instructing her to support Charles VII and recover France from English domination late in the Hundred Years’ War. The uncrowned King Charles VII sent Joan to the siege of Orléans as part of a relief mission. She gained prominence after the siege was lifted in only nine days. Several additional swift victories led to Charles VII’s coronation at Reims. On 23 May 1430, she was captured at Compiègne by the English-allied Burgundian faction, was later handed over to the English,[6] and then put on trial by the pro-English Bishop of Beauvais Pierre Cauchon on a variety of charges,[7] was convicted on 30 May 1431[8] and burned at the stake when she was about 19 years old.
Joan of Arcsin
The trigonometry arcsin() – Math Open Reference
www.mathopenref.com/arcsin.html
Inverse sine calculator. Enter the sine value, select degrees (°) or radians (rad) and press the = button. … Home>Calculators>Math Calculators> Arcsin calculator
Graphing arcsin(x) functions

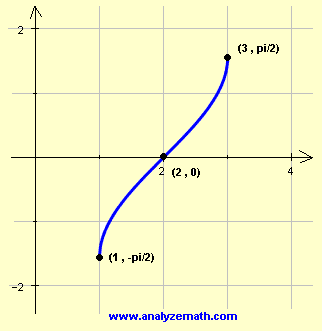
Example 1: Find the domain and range of y = arcsin(x – 2) and graph it.
Solution to Example 1:
The graph of y = arcsin(x – 2) will be that of arcsin(x) shifted 2 units to the right. The domain is found by stating that -1 ≤ x – 2 ≤ 1. Solve the double inequality to find the domain:
1 ≤ x ≤ 3
The 3 key points of arcsin(x) can also be used in this situation as follows:
| x – 2 | -1 | 0 | 1 |
| y = arcsin(x-2) | -π/2 | 0 | π/2 |
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 |
The value of x is calculated from the value of x – 2. For example when x – 2 = -1, solve for x to find x = 1 and so on.
The domain is given by the interval [1,3] and the range is given by the interval [-pi/2,pi/2]
The three points will now be used to graph y = arcsin(x – 2).




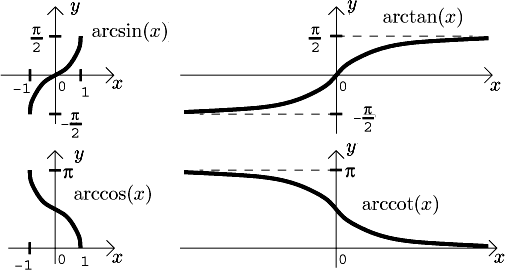

Thus we have some clues about ….
Theory of everything – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theory_of_everything
Wikipedia
A theory of everything (ToE) or final theory, ultimate theory, or master theory refers to the hypothetical presence of a single, all-encompassing, coherent …
Exceptionally Simple – Disambiguation – Philosophy
Supersymmetry is part of a larger enterprise of theoretical physics to unify everything we know about the physical world into a single fundamental framework of physical laws, known as the quest for a Theory of Everything (TOE). Wikipedia
Explore: Supersymmetry